How can you find the formal charge of an atom or molecule?
I will start with this, the formal charge of an atom is not the same as its net charge. That is, in O2-, -2 is the net charge, not the formal charge. The formal charge is not the exact charge of an atom. It is deduced assuming that electrons are shared equally in the molecule.
The formal charge is referred to as the “fake charge”. One surprising thing about the formal charge is how bonds can make two similar atoms have different formal charges.
For instance, in SO32-, the double-bonded oxygen has a formal charge of 0 and the two single-bonded oxygen atoms have a formal charge of -1 each. Several other factors also influence the formal charge of an atom. Now, how can you find the formal charge of any atom or molecule? Find out in this article.
What is a formal charge?
Formal charge is the theoretical or hypothetical charge on an atom of a molecule or ion assuming that all electrons involved in the chemical bonds are evenly distributed between the atoms, their electronegativities notwithstanding.
It also refers to the difference between the valence electrons of an atom and the number of electrons assigned to it in the Lewis structure. Formal charge helps to determine the reactivity and structure of a molecule or ion.
For molecules that have more than one Lewis structure, the structure with the least formal charges is usually preferred over the others.
Mathematically,
FC = V – L – B/2
- FC is the formal charge
- V is the total number of valence electrons
- L is the number of lone pair or non-bonding electrons
- B is the number of bonding electrons
How to find formal charges
I will be showing you how to find formal charges using three molecules: SO2, NH3, and SO32-
FC = V – L – B/2
Formal charges for SO2
Start with writing out the structure of the molecule

Starting with S,
Sulfur has 6 valence electrons, 2 lone pair electrons, and 6 bonding electrons
FC = 6 – 2 – 6/2
= 6 – 5 = 1
For the double-bonded O,
V = 6, L = 4, B = 4
FC = 6 – 4 – 4/2
= 0
For the single-bonded O,
V = 6, L = 6, B = 2
FC = 6 – 6 – 2/2
= -1
The net formal charge is 1 + 0 + (-1) = 0
Formal charges for NH3
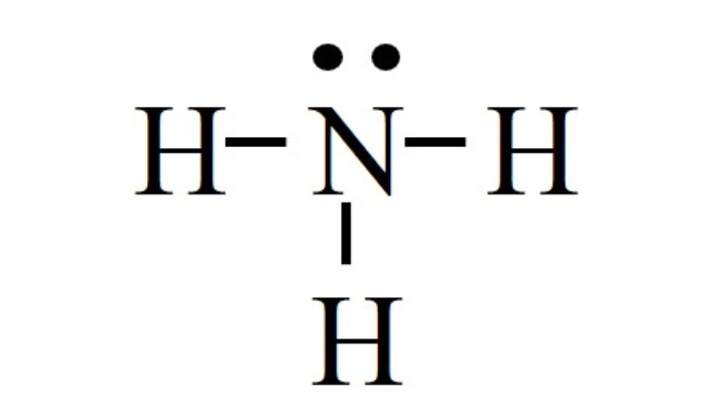
For N,
V = 5, L = 2, B = 6
FC = 5 – 2 – 6/2
FC = 0
For H,
V = 1, L = 0, B = 2
FC = 1 – 0 – 2/2
FC = 0
The net formal charge is 0 + 3(0) = 0
Formal charges for SO32-
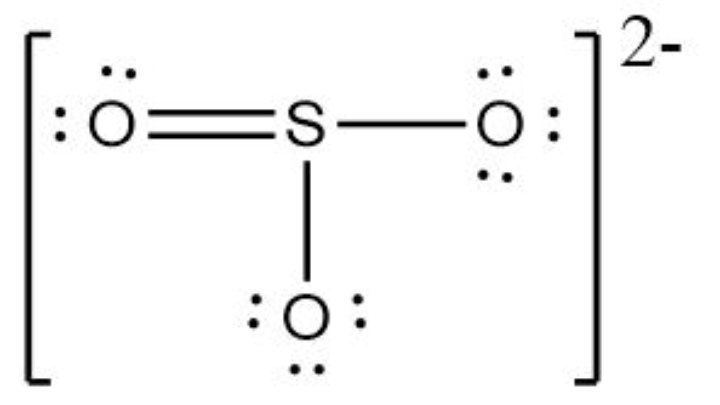
For S,
V = 6, L = 2, B = 8
FC = 6 – 2 – 8/2
FC = 0
For double-bonded O,
V = 6, L = 4, B = 4
FC = 6 – 4 – 4/2
FC = 0
For the two single-bonded O,
V = 6, L = 6, B = 2
FC = 6 – 6 – 2/2
FC = -1
The net formal charge is 0 + 0 + (-1) + (-1) = 0 – 1 – 1 = -3
What are the factors that influence the formal charge of an atom?
The formal charge is influenced by:
- The number of valence electrons of the atoms
- The number of lone pairs of electrons that do not get into the chemical reaction. More lone-pair electrons result in a more negative formal charge
- Number of bonded electrons in covalent bonds and number of covalent bonds
- Electronegativity of the element
- The position of the element on the periodic table
- Charge distribution in resonance structures
- The charge on the molecule or ion
- Hybridization of orbitals. Hybridization influences the distribution of charge in a molecule
- Atoms surrounding the atom of concern. These atoms can influence electron density on the atom of concern
What are the assumptions of the formal charge rule?
The formal charge rule assumes that:
- Electrons involved in a chemical bond are shared equally between the atoms, their electronegativity notwithstanding
- The number of valence electrons for each atom corresponds with its group number on the periodic table
- According to the Lewis model, electrons are either shared between atoms or exclusively belong to the atom on which they reside
- Electronegative atoms are more likely to bear a negative charge and electropositive atoms are likely to bear a positive charge
- The sum of all formal charges on a neutral molecule must be equal to zero and the sum of all formal charges on a polyatomic ion must be equal to the charge on the ion
What is the relationship between formal charge and oxidation number?
Formal charge and oxidation number are different concepts but, they both provide information on the distribution of electrons in molecules and ions and the electronic configuration of an element.
They are calculated differently but can be the same values for the same molecules or ions. However, while formal charge centers on the distribution of electrons in the Lewis structure, oxidation number considers electron transfer in chemical reactions via the valence electrons.
Furthermore, the formal charge of an atom can help determine the oxidation number of molecules with multiple resonance structures.
The formal charge will not correspond with the oxidation number when the compound of concern is a resonance or coordination complex.
Despite the similarities and relationships between both concepts, they have separate applications in different contexts.
Is there any relationship between formal charge and octet rule?
Yes, both concepts are related because they provide an understanding of the distribution of electrons in molecules and ions. Both rules play crucial roles in determining the structure of molecules and ions.
However, the octet rule takes precedence over the formal charge rule. When drawing the structures of molecules or ions, the first rule you should satisfy is the octet rule.
Afterward, you can move on to distributing formal charges and ensuring they are kept minimal, close to zero.
But, keep in mind that there will be exceptions. In some structures, based on the distribution of charges and the electronic properties of the elements, you may have satisfied the octet rule and may not be able to keep formal charges minimal.
FAQs
Is formal charge the same as ionic charge?
No, it is not. The formal charge is not the actual charge of an atom, whereas the ionic charge is the actual charge.
Formal charge assumes that the total bonding electrons are equally distributed over the ion or molecule. On the other hand, the ionic charge is the charge on an ion when the atom has lost or gained electrons.
What is the difference between formal charge and nuclear charge?
The formal charge is a fake charge, while the nuclear charge is the total charge or number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
What is the difference between a formal charge and Zeff?
A formal charge is a theoretical charge on one atom of an ion when the overall charge of that ion is equally distributed over the entire ion. Zeff is the overall positive charge the nucleus has on the valence electrons.
Conclusion
So, you have seen that formal charge is not the actual charge of the atom of an element. It is also not the same as the valency and oxidation state. However, in some cases, they may have similar values. This does not make them the same properties.
As said earlier, formal charge is the theoretical charge over an atom, assuming that the electrons in its bonding pairs are equally distributed among all atoms.
The formal charge also provides information on the structure of molecules, such that when a molecule has more than one structure, the structure with the least formal charges becomes more preferred.
You can also learn how to determine the effective nuclear charge, Zeff of an element.
Thanks for reading.
